Projects
Sustainable vegetable oil and biofuel from jatropha seeds
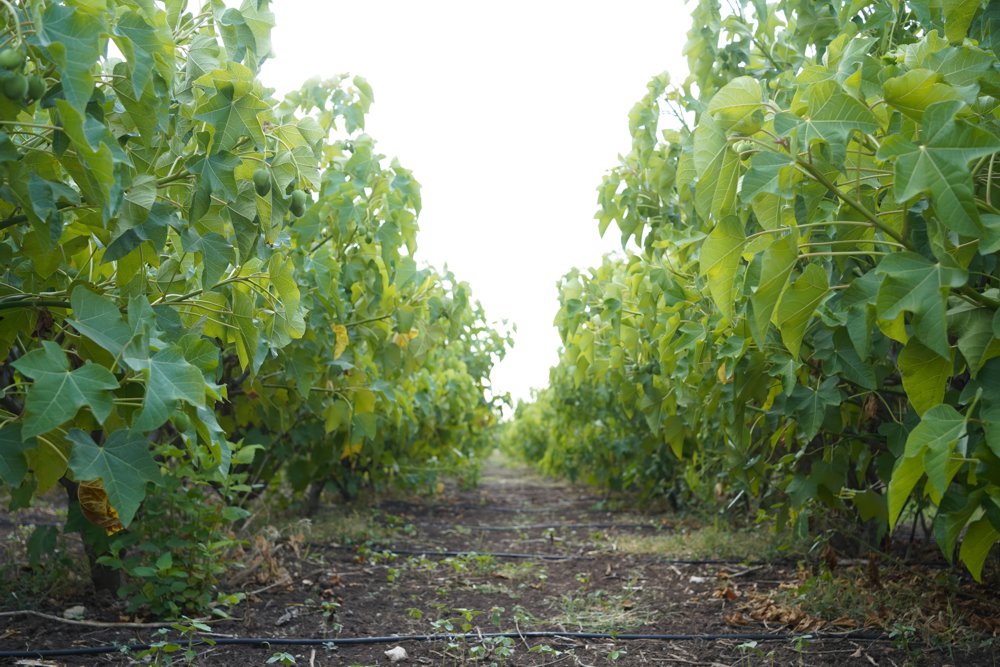
About Jatropha curcas L.
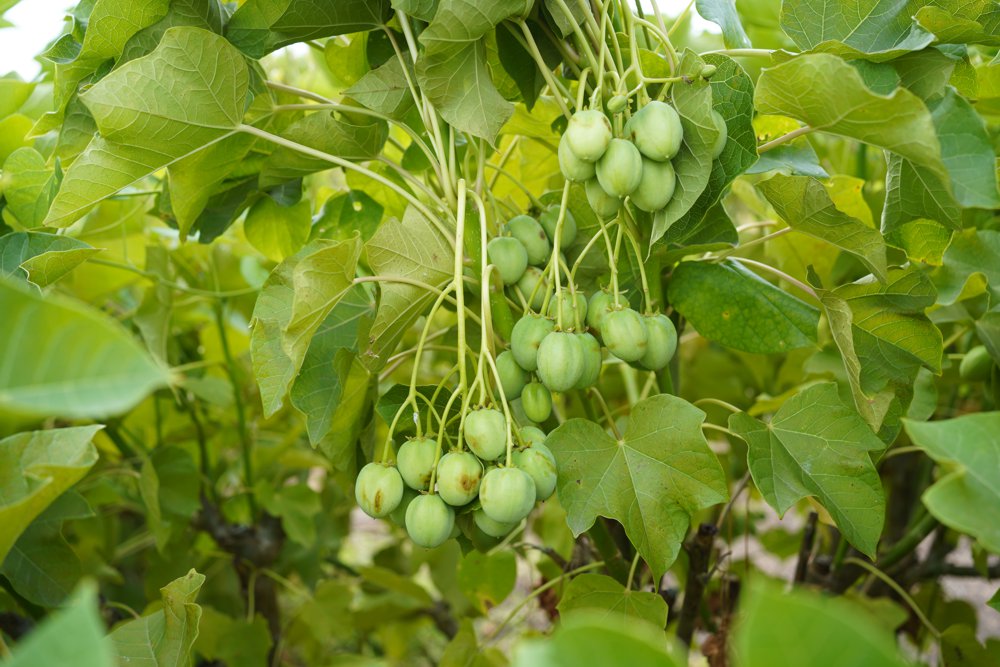
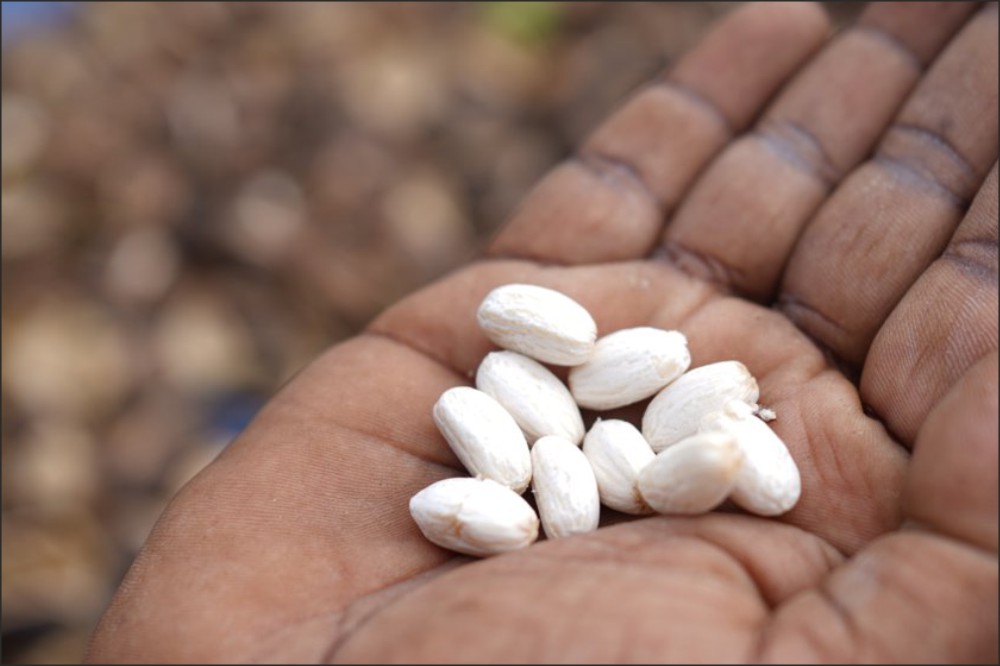
Jatropha curcas (purging nut) is a shrub or small tree belonging to the Euphorbiaceae family. It is widely distributed in tropical regions of Africa, Asia and Latin America. Its seeds have an extractable oil content of approximately 35 %.
The plant is generally toxic; however, non-toxic, edible Jatropha varieties do occur in nature. The difference between toxic and non-toxic Jatropha lies in the presence of secondary plant compounds, known as phorbol esters, in the seeds and other plant parts.
Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, Jatropha oil has high potential for fuel production. It can be used as a pure plant-oil fuel in modified engines, as a feedstock for biodiesel (according to European and ASTM standards), sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) and for the production of hydrotreated vegetable oil (HVO), which is also referred to as renewable diesel.
Benefits of Jatropha plants
- They can grow even on barren soils in semi-arid climates, without competing with land typically used for food production.
- Jatropha plantations improve the microclimate in arid regions.
- With their root characteristics and adaptability, they require relatively less irrigation and help prevent soil erosion.
- The oil is a highly promising sustainable energy source.
- Thanks to their modest requirements and robustness, they can contribute to reforestation of infertile lands.
With the availability of superior seeds and improved seed processing techniques, Jatropha cultivation is economically viable (more info here: www.jatropower.com).
The Project
In the framework of a ZIM-funded project (German Central Innovation Programme for SMEs), a raw material is to be derived from the energy plant Jatropha curcas, intended to substitute other plant oils and fossil derived oils used in the chemical industry, such as tropical coconut and palm oil, domestic rapeseed and sunflower oil or fossil-derived raw material.

In project implementation, the entire value chain is covered, from breeding and cultivation of the plants in a hot, semi-dry region to processing and oil extraction, right through to product development.
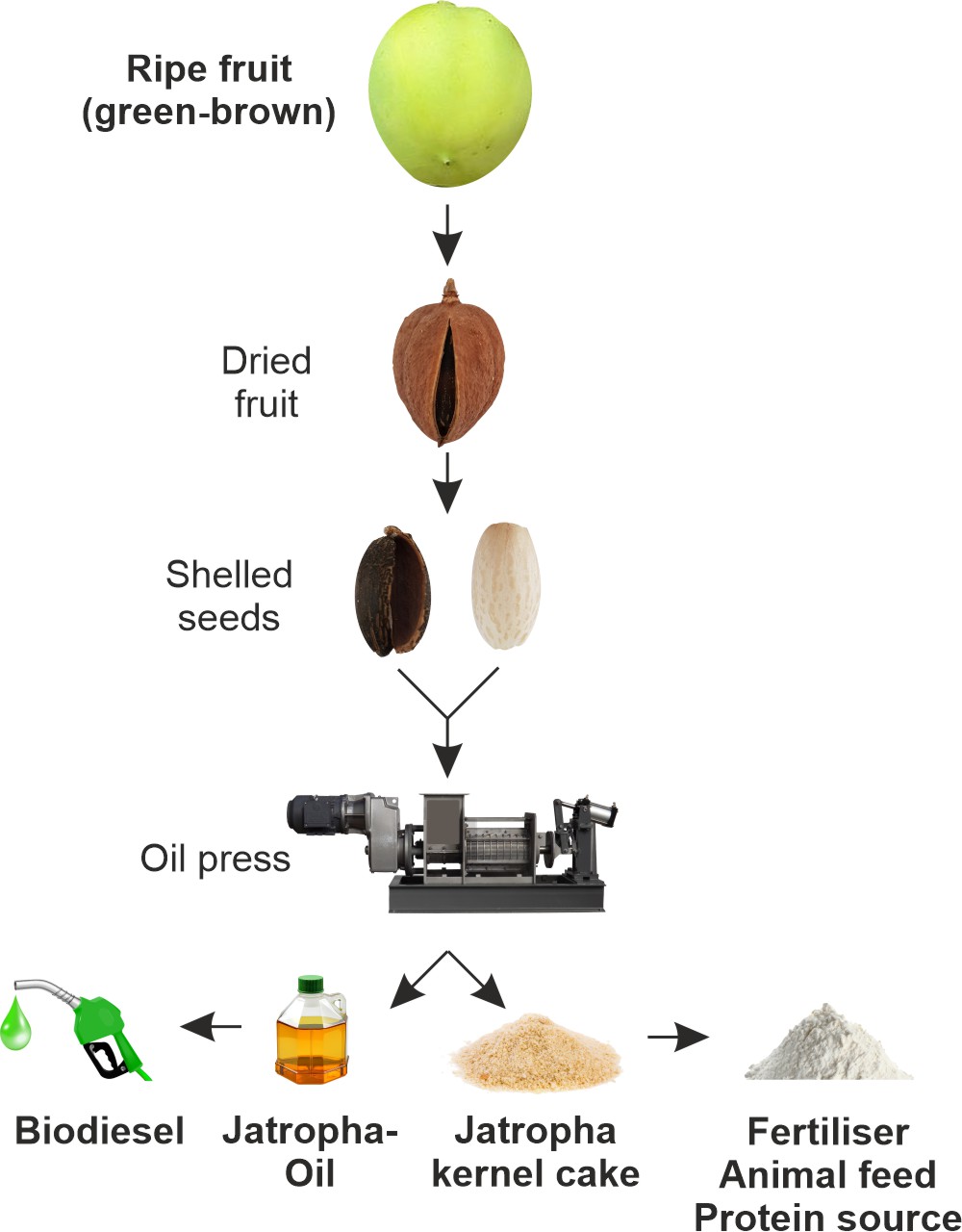
In the project, Live Energies GmbH is developing the production process for sustainable Jatropha oil, from seed conditioning through decentralised oil pressing to conditioning the oil cake as organic fertiliser, and ensuring quality-assured transport logistics from the plantation site to the processor in Germany.
Live Energies possesses knowledge derived from many years of academic research as well as practical experience in all aspects of the value chain for Jatropha curcas cultivation and agribusinessagronomy. In the past, Live Energies organised and implemented a project in which the planting of Jatropha on smallholder farms of less than 1 ha per farm was supported across a total area of 250 ha with micro-loans.
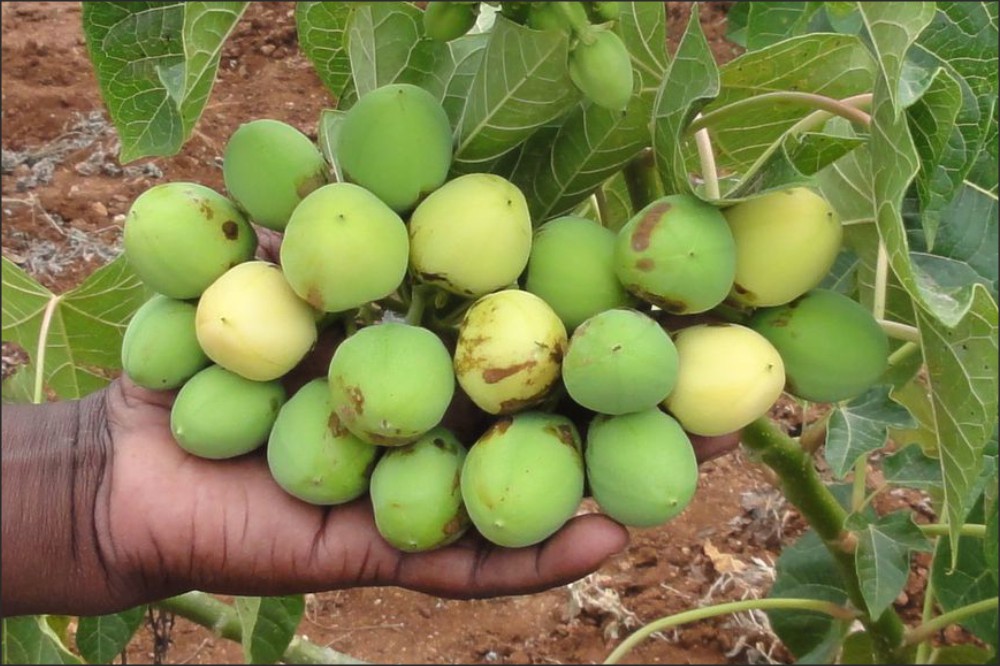
Live Energies works closely with Jatropower AG in developing high-performance edible and conventional Jatropha seeds and associated agronomic technologies. With yields four times higher than wild seed, Jatropha oil is free from “food vs fuel” controversies and ILUC (Indirect Land Use Change) conflicts and is intended for use as a CO₂-neutral raw material in ecologically certified washing and cleaning products.
Summary
-
Jatropha curcas is a tropical shrub with oil-rich seeds, whose oil is suitable as a plant-oil fuel, biodiesel, aviation fuel and HVO.
-
The plant grows on barren, semi-arid soils without competing with food production, improves the microclimate, combats erosion and requires relatively less water.
-
Newly bred varieties achieve four times higher seed yields on semi-arid land compared to wild seed.
-
A ZIM-funded project is establishing Jatropha curcas as a CO₂-neutral substitute oil for coconut, palm, rapeseed and sunflower oil in the chemical industry, avoiding “food vs fuel” and ILUC conflicts.
-
Live Energies GmbH is responsible for seed processing and quality control, decentralised oil pressing, use of oil cake as organic fertiliser and quality-assured logistics to the processor in Germany.
Project description in tabular form
Publikationen:
- Grünwald, M., Francis, G., Esatbeyoglu, T., (2025) Evaluation of the genotoxic potential and minimisation of antinutrients in edible Xuta (Jatropha curcas L.) kernels, Food and Chemical Toxicology, 204, 115624, ISSN 0278-6915, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2025.115624.
- Francis, G., Makkar, H.P.S., Carle, R. et al. Critique on conclusions regarding toxic compounds in Jatropha curcas kernel cake. Nature Commun Biol 4, 1348 (2021). >>>
- Francis, G., John, O., Piergiorgio, S., & Mulpuri, S. (2020). Apomixis as a tool for development of high yielding clones and selections in Jatropha curcas L. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 67(3), 727-743. >>>
- Trebbi, D., Ravi, S., Broccanello, C., Chiodi, C., Francis, G., Oliver, J., … & Stevanato, P. (2019). Identification and validation of SNP markers linked to seed toxicity in Jatropha curcas L. Scientific reports, 9(1), 10220. >>>
- Edible jatropha is a source of multipurpose oil and high quality protein cake that can help the tropics go beyond meat: Beyond
biofuels. Biofuels International, July/August 2019.
Projekte
Karbonisierung ↵
Jatropha
Biogas ↵








